Light reflection functions are used to (1) totally reflect light like a mirror and (2) prevent glare for requirements of anti-glare properties. As for the anti-glare properties, while the most superficial layer is bright-plated, reflection is prevented by forming microscopic projections and depressions on the base surface or by forming projections and depressions by composite plating in which fine particles are co-deposited on the primary plating.
| Type of plating | Characteristic value | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Specular reflection plating [1] Bright nickel-chromium plating [2] Bright nickel-gold plating [3] Rhodium plating |
- Silver > Gold > Copper > Aluminum ≒ Platinum ≒ Rhodium ≒ Chromium > Nickel For details, see the illustration below. |
Road safety convex mirrors, aluminum mirrors for building interior and exterior, copiers, reflecting telescopes |
| (2) Anti-glare plating [1] Bright nickel-chromium plating [2] Black chromium plating |
- Metal bases are roughed by sandblasting or shotblasting. - Projections and depressions are formed by co-depositing fine particles on the most superficial surface of plating. - The principle of light absorption is used. |
- Automotive safety standards (U.S., Canada, and Australia) |

Zinc-nickel alloy plating
(Trivalent black chromate treated)
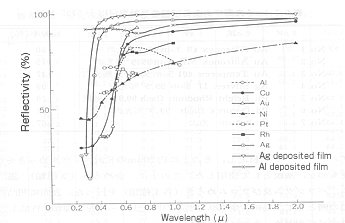
Reflectivity of major metals
(From “Mekki Gijutsu Manyuaru” edited by Tokuzo Kanbe, Japanese Standards Association)