Silver plating, which would be used for decorative purposes, dishes, dental therapy, etc., due to its [1] distinctive luminous white color and [2] antibacterial action and cleanliness, has recently been used for many parts of electrical and electronic devices due to its excellent [3] electrical conductivity, [4] solderability, and [5] bondability. It also plays an active part in the field of machine parts due to its [6] good thermal-resistant baking seal properties, etc.
| Type of plating | Features (characteristic value) | Characteristic value |
|---|---|---|
| Alkaline cyanide silver plating (1) Dull bath (2) Semigloss/bright bath (3) Strike bath |
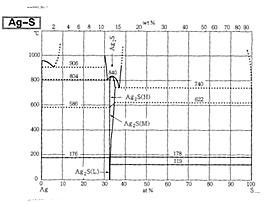
- The electrical conductivity of silver is the highest among practical metals. (Ag > Cu > Au > Al > Ni > Fe > Pt > Pb) - Hard silver plating for connectors, terminals, and switches. Soft silver plating for IC lead frames. - Bondability and solderability are both good. - Silver is the most human-friendly metal with antibacterial action. - The only disadvantage is its tendency for discoloration. In particular, it has high sulfur sensitivity. Silver sulfide is generated, resulting in black discoloration. |
Hv70 – 90 (soft), Hv110 – 130 (hard) |
| Electroless plating bath | Replacement type electroless silver plating (primary copper plating) | |
| Silver mirror reaction (Silver nitrate + ammonia solution + reducing agent) |
Utilized as a plating method to manufacture glass mirrors and give conductivity to resins. | |
Silver-sulfur binary phase diagram